Hello Everyone!
Today, I am writing a longer deep dive format, which is longer than my usual writeups, I hope this will give you an insight from my brain about the company I consider to be the best in the world - COST 0.00%↑ .
Introduction to Costco
Costco Wholesale Corporation ( COST 0.00%↑ ) is one of the best comapnies in the retail industry in the entire world. Famous for its membership-only warehouse clubs that offer a vast array of products at competitive prices, since its inception in 1983 in Seattle, Washington, Costco has expanded globally, becoming a staple in both consumer shopping habits and investment portfolios.
How I Got Introduced to Costco
My initial exposure to Costco was through Charlie Munger, who famously stated he would never sell a share of Costco (which he never did btw)—showing confidence in the company. This made me curious, and during my time in the U.S., I became a regular Costco shopper. The experience was distinctive: happier employees (than Walmart), low prices, a lot of tasting offerings, and of course the iconic $1.50 hot dog combo—a deal that has remained unchanged for decades. The shopping experience is rewarding as it encourages people to find the best deal and gives that dopamin hit when they find it - just like playing games or solving puzzles.
I have been buying COST 0.00%↑ stock ever since I have started investing and haven’t sold a share yet. Here is how my COST 0.00%↑ preformance looks like:
📊 Deep Dive into Costco
1. Company Overview
Business Model: Costco operates on a unique membership-based (my favorite type - predictable nature) warehouse model, distinguishing itself from traditional retailers. Members pay an annual fee—ranging from $60 for a basic Gold Star membership to $120 for an Executive membership—to access Costco’s wide range of products at discounted prices and benefits. This dual revenue stream model, where the company generates income from both membership fees and product sales, creates a financial moat. Membership fees alone accounted for approximately $4.8 billion in revenue in fiscal year 2024, representing a highly stable and recurring income source that cushions the company against economic fluctuations.
What makes this model brilliant is its inherent stickiness as subscribers/members are more likely to spend and more likely to spend higher. With a renewal rate exceeding 90% globally, Costco has unmatched customer loyalty. The razor-thin margins on goods—often around 11%—are strategic. By pricing products competitively, Costco drives massive sales volumes. This "high volume, low margin" approach is sustainable because membership fees cover a significant portion of the company’s operating profits, allowing Costco to maintain aggressive pricing without sacrificing profitability.
Additionally, Costco’s limited SKU strategy is a key differentiator. Unlike traditional supermarkets that may carry 30,000+ items, Costco stocks around 3,700 carefully curated products. This focus reduces complexity, enhances inventory turnover (which averages around 28 days), and strengthens Costco’s bargaining power with suppliers, further driving down costs. Meanwhile, for customers, it ensures they don’t have decision fatigue, plus the quality Costco has been delivering ensures the limited SKU isn’t a problem for the customers.
Products/Services: Costco offers almost everything - an extensive and diverse product lineup, ranging from everyday essentials to luxury items. Its core offerings include:
Groceries: Fresh produce, meats, dairy, and pantry staples sold in bulk at competitive prices.
Electronics: TVs, laptops, and home appliances, often bundled with extended warranties.
Home Goods & Apparel: Furniture, bedding, clothing, and seasonal items.
Pharmaceuticals: Prescription medications and over-the-counter health products through Costco Pharmacy.
Financial & Travel Services: Costco Travel offers vacation packages, car rentals, and cruises, while its financial services include insurance and mortgage options.
Unusual Offerings: From fine wines and caviar to caskets and even gold bars (which was recently getting popular)—yes, you can buy gold at Costco!
A standout feature is Kirkland Signature, Costco’s private-label brand launched in 1995. Known for exceptional quality at lower prices, Kirkland products are often manufactured by top-tier brands under Costco’s label. In 2024, Kirkland accounted for approximately 31% of Costco’s total sales. Its success lies in Costco’s ability to maintain rigorous quality standards while offering products at a 20-30% discount compared to national brands. I have loved Krikland wines personally.
History: Costco’s story began in 1983 when James Sinegal and Jeffrey Brotman opened the first warehouse in Seattle. However, its roots trace back to Price Club, founded by Sol Price in 1976, which pioneered the membership warehouse concept. In 1993, Costco and Price Club merged, creating PriceCostco, which later became simply "Costco." This merger blended operational excellence with innovative retail strategies, propelling the company’s rapid growth.
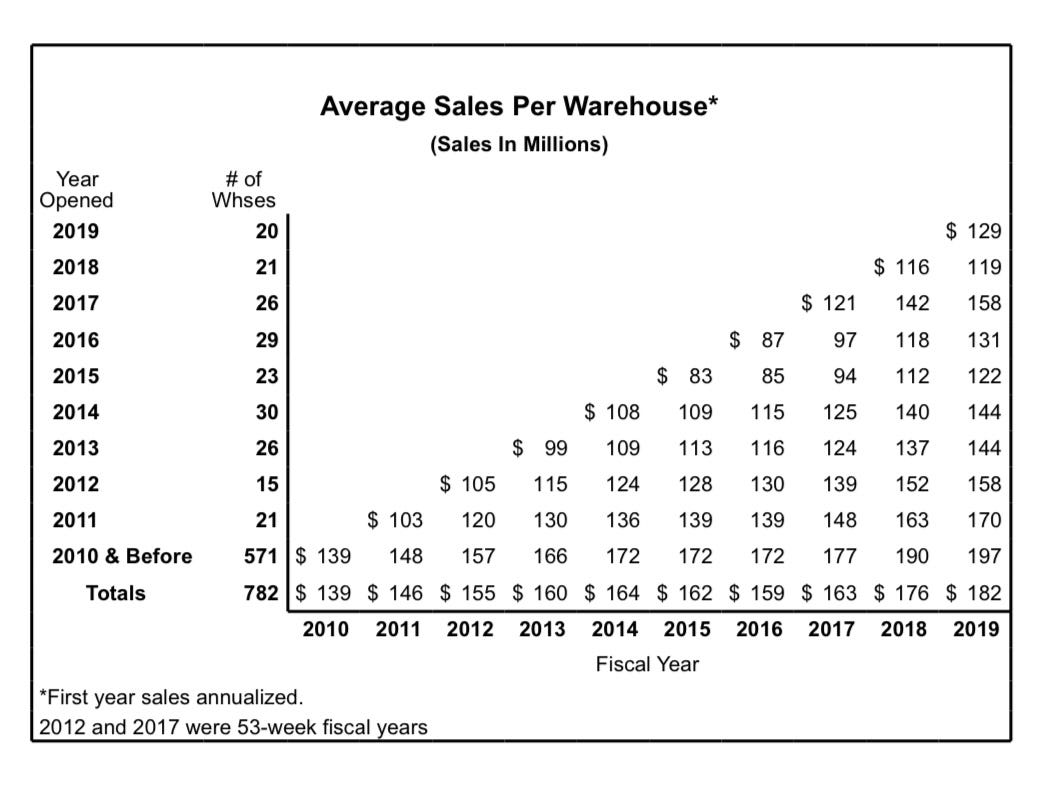
Since then, Costco has expanded to 890 warehouses globally as of 2024, including locations in:
United States: Over 570 locations, the largest market.
Canada & Mexico: Strong presence with dedicated supply chains.
Asia-Pacific: Rapid growth in Japan, South Korea, China, and Australia.
Europe: Emerging markets, with a growing footprint in the UK, Spain, and France.
Costco’s growth has been organic, driven by word-of-mouth rather than traditional advertising, which aligns with its cost-saving ethos. The company’s "treasure hunt" shopping experience—where inventory rotates frequently to surprise customers—creates a sense of urgency and excitement, encouraging repeat visits.
Mission & Vision: Costco’s mission is clear and unwavering:
"To continually provide our members with quality goods and services at the lowest possible prices."
This simple yet powerful statement is more than just corporate jargon—it’s embedded in Costco’s DNA. Every strategic decision, from supplier negotiations to employee benefits, aligns with this mission. The company’s vision extends beyond profit, focusing on ethical business practices, sustainability, and employee welfare.
Costco is also committed to operational excellence through:
Efficiency: Streamlined supply chains and inventory management.
Sustainability: Reducing environmental impact through energy-efficient warehouses and ethical sourcing.
Employee Welfare: Competitive wages and benefits, contributing to low turnover and high employee satisfaction.
In essence, Costco’s success isn’t accidental. It’s the result of a disciplined, principled approach that prioritizes value for members, operational efficiency, and long-term growth.
💸 Financial Performance
Costco’s financial performance in fiscal year 2024 reflects the company’s resilience, operational efficiency, and the strength of its unique business model. Let’s break down the key financial metrics that paint a comprehensive picture of Costco’s fiscal health:
Revenue Growth: In fiscal year 2024, Costco reported net sales of $249.6 billion, marking a 5% increase compared to the previous year. This impressive growth was fueled by multiple factors:
Foot Traffic Surge: Year-over-year foot traffic increased by 10.6%, driven by strong demand for bulk goods, competitive pricing, and the "treasure hunt" shopping experience that keeps members coming back.
Global Expansion: The addition of 29 new warehouses, particularly in high-growth markets like China and Japan, contributed to revenue growth.
E-commerce Boom: Online sales grew by 16.1%, showcasing Costco’s ability to adapt to digital retail trends without compromising its in-store experience.
Costco’s ability to maintain growth even during challenging macroeconomic conditions, such as inflationary pressures and supply chain disruptions, highlights its robust business model.
Profitability: Costco’s profitability metrics are a testament to its operational efficiency and strategic cost management:
Net Income: Costco posted a net income of $7.4 billion in fiscal 2024, translating to $16.56 per diluted share. This represents a 17% increase from the prior year.
Gross Margins: Despite its low-price strategy, Costco maintains a healthy gross margin of around 11%. This is achieved through high sales volume, efficient supply chain management, and cost savings from private-label products like Kirkland Signature.
Operating Margin: Consistently around 3.5%, reflecting disciplined cost control while investing in growth initiatives.
Membership Revenue: Membership fees are Costco’s secret weapon, providing a steady, high-margin revenue stream:
Membership Fee Revenue: In 2024, Costco generated $4.8 billion in membership fees, a 5% increase from the previous year.
Membership Base: The total number of cardholders grew to nearly 137 million, with an impressive renewal rate of 90% globally. In North America, renewal rates are even higher, hovering around 92%, reflecting strong customer loyalty.
Executive Membership Growth: Executive memberships, which cost double the standard membership but offer 2% cash back on purchases, continue to grow rapidly, contributing significantly to overall revenue.
Key Financial Ratios: Costco’s financial health is further highlighted by key ratios that reflect its valuation, efficiency, and stability:
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: As of February 2025, Costco’s P/E ratio stands at approximately 59.06. This relatively high multiple indicates strong investor confidence in Costco’s future growth prospects, supported by consistent earnings growth and a resilient business model.
Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio: Costco’s P/S ratio is 1.56, reflecting its premium valuation compared to other retailers. Investors are willing to pay more for each dollar of Costco’s sales due to its stable revenue streams, membership model, and growth potential.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Costco maintains a conservative debt-to-equity ratio of 0.31, emphasizing its prudent approach to leverage. The company’s low debt levels provide financial flexibility, reducing risk during economic downturns.
Return on Equity (ROE): Costco boasts a strong ROE of 28%, showcasing its ability to generate significant profits from shareholders’ equity. This is driven by efficient asset utilization, high inventory turnover, and strong membership retention.
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC): Costco’s ROIC stands at 15%, indicating effective capital allocation and a competitive advantage in generating returns on investments.
Free Cash Flow (FCF): Costco’s free cash flow remains robust, providing flexibility to invest in growth initiatives, dividends, and share buybacks. In 2024, Costco generated approximately $5.1 billion in FCF, supporting:
Dividend Growth: Costco paid an annual dividend of $4.08 per share, with a history of consistent increases.
Share Buybacks: The company repurchased $1.5 billion worth of shares in 2024, signaling confidence in its long-term value.
Inventory Turnover: Costco’s inventory turnover ratio is around 12 times per year, meaning the company sells and replaces its inventory approximately every 28 days. This high turnover rate minimizes holding costs, enhances cash flow, and reduces the risk of inventory obsolescence.
📈 Growth Drivers
Costco’s growth story is far from over. In fact, the company’s business model and strategic initiatives suggest a long runway for expansion. Here’s a closer look at the key growth drivers fueling Costco’s continued success:
Total Addressable Market (TAM): Costco’s TAM is vast, encompassing the global retail landscape. The wholesale club industry alone is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by rising consumer demand for bulk buying and value-based shopping. Costco currently operates in 14 countries but has only scratched the surface in several high-potential markets like China and parts of Europe.
Global Retail Market: Estimated at over $30 trillion, even capturing a small percentage of this market represents a massive growth opportunity.
Underpenetrated Regions: Asia, particularly China and India, presents immense potential. Costco’s initial stores in China have seen overwhelming demand, with memberships selling out rapidly.
Urban Expansion: As urbanization increases globally, Costco’s flexible warehouse formats allow it to adapt to densely populated areas, tapping into new customer bases.
Emerging Trends: Costco’s business model is perfectly aligned with several emerging retail trends that are reshaping consumer behavior:
Value-Based Shopping: In an era of economic uncertainty and inflation, consumers are prioritizing value. Costco’s low-price, high-quality offerings make it a go-to destination for budget-conscious shoppers.
Private-Label Growth: The rise of private-label products is a major trend, and Costco’s Kirkland Signature brand is a standout performer, contributing around 31% of total sales. Consumers trust Kirkland for its quality and affordability.
Sustainability and Health Consciousness: Growing demand for organic, sustainable, and health-conscious products aligns with Costco’s expanding offerings in these categories. The company’s focus on sustainable sourcing and eco-friendly practices enhances its brand appeal.
Expansion Plans: Costco’s disciplined expansion strategy is a key driver of its growth:
New Warehouse Openings: In fiscal 2024, Costco opened 29 net new locations:
23 in the U.S. – strengthening its dominant position.
2 each in China and Japan – tapping into high-growth international markets.
1 each in Canada and South Korea – reinforcing its presence in established regions.
International Growth: Costco’s entry into China has been particularly promising. The company’s Shanghai store reportedly attracted over 200,000 memberships shortly after opening. Plans to expand further in Asia, including India and Southeast Asia, are in motion.
Urban Format Stores: Experimenting with smaller, urban warehouse formats to capture new demographics in city centers.
E-commerce Growth: While Costco’s traditional business thrives on in-store experiences, its e-commerce segment is rapidly expanding:
Online Sales Growth: E-commerce sales grew by 16.1% in 2024, driven by improvements in the online shopping experience and increased product availability.
Omnichannel Strategy: Costco’s "click-and-collect" service allows customers to order online and pick up in-store, blending the convenience of e-commerce with the efficiency of warehouse operations.
Global E-commerce Expansion: Costco is enhancing its digital footprint in international markets, especially in Canada, the UK, and China, where online shopping adoption rates are high.
Technology & Digital Transformation: Costco is investing in technology to streamline operations and improve the customer experience:
Data Analytics: Leveraging data to optimize inventory management, personalize marketing, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Mobile App Enhancements: The Costco app has seen significant growth, driving digital engagement and offering personalized deals to members.
Automation: Investments in warehouse automation and supply chain technologies to reduce costs and increase operational efficiency.
⚠️ Risks & Challenges
While Costco’s growth trajectory appears robust, it faces several risks and challenges that could impact its performance. Understanding these risks is crucial for investors seeking a comprehensive view of Costco’s future prospects.
Competitive Landscape:
Costco operates in an intensely competitive environment, facing rivals on multiple fronts:
Traditional Retail Giants: Competitors like Walmart and Sam’s Club (owned by Walmart) offer similar bulk-buying models with aggressive pricing strategies. Sam’s Club, in particular, mirrors Costco’s membership model, posing a direct threat.
E-commerce Disruptors: Amazon continues to disrupt the retail landscape with its convenience, fast delivery, and vast product selection. Costco’s lower online presence compared to Amazon could limit its reach, especially among younger, tech-savvy consumers.
Regional Players: In international markets, Costco faces strong local competitors who understand regional consumer behavior better. For example, in China, retailers like Alibaba’s Freshippo are dominant in urban areas.
Impact: Increased competition can lead to pricing pressures, shrinking margins, and potential membership churn if competitors offer more convenience or better value propositions.
Market Risks:
Costco’s performance is also tied to macroeconomic factors that are beyond its control:
Economic Downturns: While Costco’s focus on essentials provides resilience, severe recessions can still dampen consumer spending. During economic slowdowns, even loyal members may reduce discretionary purchases, impacting revenue growth.
Inflationary Pressures: Rising costs of goods, transportation, and wages can squeeze margins. Although Costco has strong supplier relationships, persistent inflation could force price increases, potentially alienating cost-conscious customers.
Currency Fluctuations: As a global company, Costco is exposed to foreign exchange risks. A strong U.S. dollar can negatively affect international sales and profitability.
Operational Risks:
Operational challenges can disrupt Costco’s ability to deliver its value proposition effectively:
Supply Chain Disruptions: Events like the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains. Delays, shortages, and increased freight costs can erode margins and lead to stockouts, impacting customer satisfaction.
Labor Shortages: With rising labor costs and increased unionization efforts in some regions, Costco may face challenges in maintaining its employee satisfaction while controlling costs. Labor disputes could also disrupt operations.
Inventory Management: Costco’s high inventory turnover is a strength, but any mismanagement can lead to overstocking or understocking, both of which have financial implications.
Company-Specific Risks:
Some risks are unique to Costco’s business model and strategic decisions:
Dependence on Membership Model: Membership fees contribute significantly to Costco’s profitability. A decline in renewal rates—due to economic conditions, increased competition, or changes in consumer preferences—could materially affect its financial health.
Regulatory Compliance: As Costco expands globally, it faces complex regulatory environments. Issues related to labor laws, data privacy, environmental regulations, and international trade policies can increase compliance costs and legal risks.
Leadership Transition: Costco has a history of strong leadership from within. However, any missteps in succession planning or strategic shifts under new leadership could disrupt the company’s culture and operational efficiency.
Technological Risks:
In today’s digital age, technology-related risks cannot be overlooked:
Cybersecurity Threats: As Costco expands its e-commerce footprint, the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks increases. A major security breach could damage customer trust and lead to significant legal liabilities.
Digital Transformation Challenges: While Costco has made strides in e-commerce, it still lags behind pure-play digital retailers. Failure to innovate or adapt quickly to technological changes could limit growth in the digital space.
💼 Management & Leadership
The leadership at Costco has been pivotal in shaping the company’s culture, operational efficiency, and long-term growth. Here’s an in-depth look at the key elements of Costco’s management strategy:
CEO: Ron Vachris
Ron Vachris assumed the role of President and CEO of Costco in 2024, succeeding Craig Jelinek. Vachris’s journey with Costco is a textbook example of the company’s "promote-from-within" culture. Starting as an entry-level warehouse employee in the late 1980s, he steadily climbed the corporate ladder through dedication and a deep understanding of Costco’s operations.
Vachris brings over 30 years of experience within Costco, having previously served as the Chief Operating Officer (COO). His operational expertise ensures that the company’s core values—efficiency, low prices, and employee satisfaction—remain at the forefront of strategic decisions. His leadership style emphasizes:
Operational Excellence: Focus on streamlining processes and maintaining Costco’s cost leadership.
People-First Approach: Prioritizing employee welfare, which has been a cornerstone of Costco’s success.
Adaptability: Balancing traditional retail strengths with the demands of e-commerce and international expansion.
Insider Ownership:
One of Costco’s standout features is the high level of insider ownership, which aligns the interests of executives with those of shareholders. This "skin in the game" mentality fosters a long-term perspective, discouraging short-term decision-making that might boost quarterly results at the expense of sustainable growth.
Key Figures: Many senior executives and board members hold substantial shares, reinforcing their commitment to Costco’s future.
Impact: Insider ownership has been linked to Costco’s conservative financial management, consistent dividend policies, and shareholder-friendly practices like regular buybacks.
Recent Strategic Moves:
Under the leadership of Vachris and his predecessors, Costco has pursued several key initiatives to drive growth and operational resilience:
Global Expansion: Costco continues to expand its footprint internationally. Recent years have seen aggressive growth in markets like China, Japan, and South Korea, with plans to enter new territories where the warehouse model shows strong potential.
Supply Chain Resilience: Learning from pandemic-era disruptions, Costco has invested heavily in strengthening its supply chain. This includes diversifying suppliers, increasing inventory levels for key items, and enhancing logistics capabilities through Costco Logistics, which was bolstered after acquiring Innovel Solutions.
Digital Transformation: While Costco’s roots are in brick-and-mortar retail, the company has accelerated its digital initiatives:
E-commerce Growth: Enhancements to the online shopping experience, including improved website functionality and expanded product offerings.
Data-Driven Operations: Leveraging analytics to optimize pricing, inventory management, and personalized marketing.
Omnichannel Strategy: Seamlessly integrating online and offline experiences to meet evolving consumer expectations.
Leadership Development & Succession Planning:
Costco’s leadership pipeline is robust, thanks to a strong emphasis on internal promotions and long-term career development. The company’s "promote-from-within" culture not only preserves its corporate values but also ensures leadership continuity. In fiscal 2024 alone, 85% of new warehouse managers were promoted internally, many of whom started as hourly employees.
Succession Planning: A key priority for Costco’s board, ensuring that future leaders are well-versed in the company’s culture and operational philosophy.
Leadership Training: Ongoing development programs for high-potential employees at all levels, fostering a deep bench of talent.
💰 Dividends & Capital Allocation
Costco’s approach to dividends and capital allocation reflects its commitment to creating long-term shareholder value while maintaining financial flexibility for growth initiatives. Here’s a closer look at how Costco manages its capital:
Dividend Yield:
Costco offers a modest but steadily growing dividend, reflecting its strong earnings growth and disciplined capital management. In 2024, the company paid an annual dividend of $4.08 per share (100%+ growth since 2017), showcasing consistent growth over the years. While Costco’s regular dividend yield may appear modest compared to traditional income-focused stocks, it’s backed by robust financial health and reliable cash flow generation.
What truly sets Costco apart, however, is its history of special dividends. Unlike many companies that stick solely to quarterly payouts, Costco occasionally rewards shareholders with substantial special dividends, often funded by excess cash reserves. For instance:
In 2020, Costco issued a special dividend of $10 per share.
In 2017, shareholders received a $7 per share special dividend.
In 2012, Costco paid a remarkable $7 per share special dividend amid favorable tax conditions.
These special dividends make Costco’s dividend policy unique, offering periodic "bonus" returns that significantly boost the overall yield for long-term investors.
Share Buybacks:
Costco engages in strategic share repurchases, reflecting management’s confidence in the company’s future growth prospects. While Costco’s buyback program isn’t as aggressive as some tech giants, it’s used effectively to:
Offset dilution from employee stock options.
Enhance earnings per share (EPS).
Signal strong financial health to the market.
In 2024, Costco repurchased approximately $1.5 billion worth of its shares, underscoring its balanced approach to capital returns.
Reinvestment Strategy:
Beyond dividends and buybacks, Costco reinvests a significant portion of its profits into initiatives that fuel long-term growth:
Store Expansion: Costco opened 29 new warehouses in fiscal 2024, with plans to continue expanding both domestically and internationally.
Technology Investments: Increased spending on e-commerce platforms, data analytics, and supply chain automation to enhance operational efficiency.
Supply Chain Improvements: Investments in Costco Logistics and distribution centers to strengthen resilience and reduce costs.
Sustainability Initiatives: Capital allocated towards renewable energy projects and eco-friendly store designs to meet environmental goals
🗓️ Recent Earnings & Guidance
Latest Results: Strong Q4 performance with a notable 23.8% post-Labor Day traffic surge. Revenue and earnings exceeded expectations.
Forward Guidance: Optimistic outlook, with management expecting strong holiday season sales and continued membership growth.
Earnings Call Insights: Focus on cost leadership, supply chain resilience, and expanding the treasure-hunt shopping experience.
🌍 Industry & Macro Trends
Sector Performance: The retail sector remains resilient, with warehouse clubs outperforming traditional retailers.
Economic Factors: High inflation and interest rates push consumers towards value-focused retailers like Costco.
Technological Disruptions: E-commerce growth and supply chain innovations are reshaping the retail landscape. Costco’s adaptability is key to maintaining its edge.
⚡ Bull & Bear Case
Bullish Thesis:
Costco’s investment appeal is deeply rooted in its strong brand loyalty, efficient operations, and global expansion potential. The company’s membership-based model provides a reliable and recurring revenue stream, with renewal rates consistently above 90% globally. This high level of customer retention is a testament to the value Costco offers its members.
Moreover, Costco’s recession-resistant business model adds to its investment allure. Unlike traditional retailers, Costco thrives even during economic downturns as consumers flock to its warehouses to save money by buying in bulk. Its focus on high-volume, low-margin sales ensures steady cash flow regardless of market conditions.
International growth presents another bullish angle. With a stronghold in North America, Costco’s recent expansions into markets like China, Japan, and South Korea have shown promising results. The company’s ability to adapt its model to diverse cultural and economic environments bodes well for long-term global growth.
Costco’s disciplined cost management, coupled with its commitment to employee welfare (offering competitive wages and benefits), results in high employee satisfaction and operational efficiency—factors that enhance both customer experience and profitability.
Bearish Thesis:
While Costco’s business model is robust, it’s not immune to risks. One of the primary concerns is economic slowdowns. Although Costco tends to perform well during recessions, severe economic downturns could still impact discretionary spending, affecting sales of higher-margin non-essential items.
Competitive pressures are another significant challenge. The retail landscape is fiercely competitive, with giants like Amazon, Walmart, Sam’s Club, and BJ’s Wholesale constantly vying for market share. Amazon’s dominance in e-commerce poses a particular threat, as Costco’s online presence, though growing, still lags behind digital-first competitors.
There’s also the risk of membership fatigue. While renewal rates are currently high, there’s no guarantee this will remain the case indefinitely. Changes in consumer behavior, driven by evolving shopping preferences or better value propositions from competitors, could lead to slower membership growth or even declines.
Lastly, Costco’s thin profit margins—a deliberate part of its low-price strategy—mean that even small increases in operating costs (like wages, transportation, or raw materials) can significantly impact profitability. Supply chain disruptions and inflationary pressures add further complexity to managing costs effectively.
My Take:
Costco’s unique business model, with its emphasis on delivering exceptional value to customers through low prices, bulk offerings, and high-quality private-label products, positions it as a robust long-term investment. Its ability to thrive in both favorable and challenging economic environments makes it a cornerstone for any diversified portfolio.
While competitive and economic risks exist, Costco’s strong brand equity, loyal customer base, and disciplined financial management provide a solid foundation for sustainable growth. Its conservative approach to debt, history of rewarding shareholders through dividends and special payouts, and strategic international expansion further strengthen its investment case.
For investors seeking a balance of stability, growth potential, and resilience, Costco remains a compelling choice. It’s not just a retail giant; it’s a company that has mastered the art of delivering value—to both its customers and shareholders.
📈 Stock Valuation: Is Costco Fairly Priced?
Valuation is key when assessing whether Costco is an attractive investment at its current price. Here’s a breakdown of Costco’s intrinsic value using two widely accepted valuation methods: the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model and the Dividend Discount Model (DDM).
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model:
The DCF model estimates Costco’s intrinsic value based on its future free cash flows, discounted back to present value. This method is especially useful for companies like Costco, which generate consistent and predictable cash flows.
Assumptions:
Free Cash Flow (2024): $5.1 billion
Growth Rate (Next 10 Years): 8% annually
Discount Rate (WACC): 9%
Terminal Growth Rate: 3% (reflecting long-term economic growth)
Results: The intrinsic value of Costco based on the DCF model is approximately $128.34 billion. This reflects the company’s strong cash flow generation, growth prospects, and conservative discounting of future earnings.
2. Dividend Discount Model (DDM):
The DDM is ideal for dividend-paying companies like Costco, especially considering its history of consistent dividend payouts and special dividends.
Assumptions:
Annual Dividend (2024): $4.08 per share
Dividend Growth Rate: 6% annually
Required Rate of Return: 8%
Results: Using the Gordon Growth Model, the intrinsic value per share is estimated at $216.24. This suggests that Costco’s reliable dividend stream, coupled with growth potential, adds significant value for long-term income-focused investors.
📈 Valuation: Is Costco Expensive?
When compared to historical averages, Costco’s current valuation appears expensive relative to its historical norms:
P/E Ratio (Current): ~59.06, significantly higher than its 10-year historical average of around 30-35. This suggests that the market is pricing in strong future growth expectations.
P/S Ratio (Current): 1.56, which is above the pre-pandemic average of around 0.8-1.0, reflecting investor confidence in Costco’s resilience and growth potential.
Despite trading at a premium (which normally it does - I have heard from 2019 to today that Costco is expensive/premium), this valuation is justified given Costco’s:
Consistent double-digit revenue and earnings growth.
Strong membership retention rates (over 90%).
Resilience in economic downturns due to its focus on essential goods.
However, for value-oriented investors, it may be considered overvalued based purely on traditional valuation metrics. The premium reflects Costco’s robust business model, growth prospects, and shareholder-friendly capital allocation strategy.
Key Takeaways:
DCF Model: Highlights Costco’s robust free cash flow generation and long-term growth potential, valuing the company at $128.34 billion.
DDM: Reflects the company’s shareholder-friendly dividend policy, estimating an intrinsic value of $216.24 per share.
While Costco may seem expensive based on historical valuation multiples, its strong fundamentals, global growth prospects, and operational efficiency may justify the premium for long-term investors.
🧠 Final Thoughts
Costco isn’t just a store; it’s a well-oiled machine with an unbeatable value proposition. It embodies the principle that success doesn’t always come from complexity—sometimes, it’s the simple things done exceptionally well that create lasting impact. Whether it’s Charlie Munger’s unwavering belief in the company, my own experiences as a satisfied shopper, or the impressive financials that consistently outperform expectations, Costco proves that simplicity, efficiency, and customer obsession are timeless business virtues.
What makes Costco truly fascinating is its ability to blend frugality with quality—offering premium products at unbeatable prices while running an ultra-lean operation. This is a company that turns over its inventory at lightning speed, keeps its margins razor-thin, yet manages to generate billions in profits, reward shareholders with special dividends, and maintain a fiercely loyal customer base.
For investors, Costco represents more than just a stock. It’s a compounding machine, driven by disciplined leadership, an unmatched business model, and a culture rooted in operational excellence. Its resilience during economic downturns, strategic international growth, and commitment to both employees and customers make it a cornerstone in any well-diversified portfolio.
So, whether you’re a fan of their giant tubs of peanut butter, their legendary $1.50 hot dog combo, or their stellar dividend history—Costco delivers. It’s not just about what’s on the shelves; it’s about the business behind them. And that business is built to last.